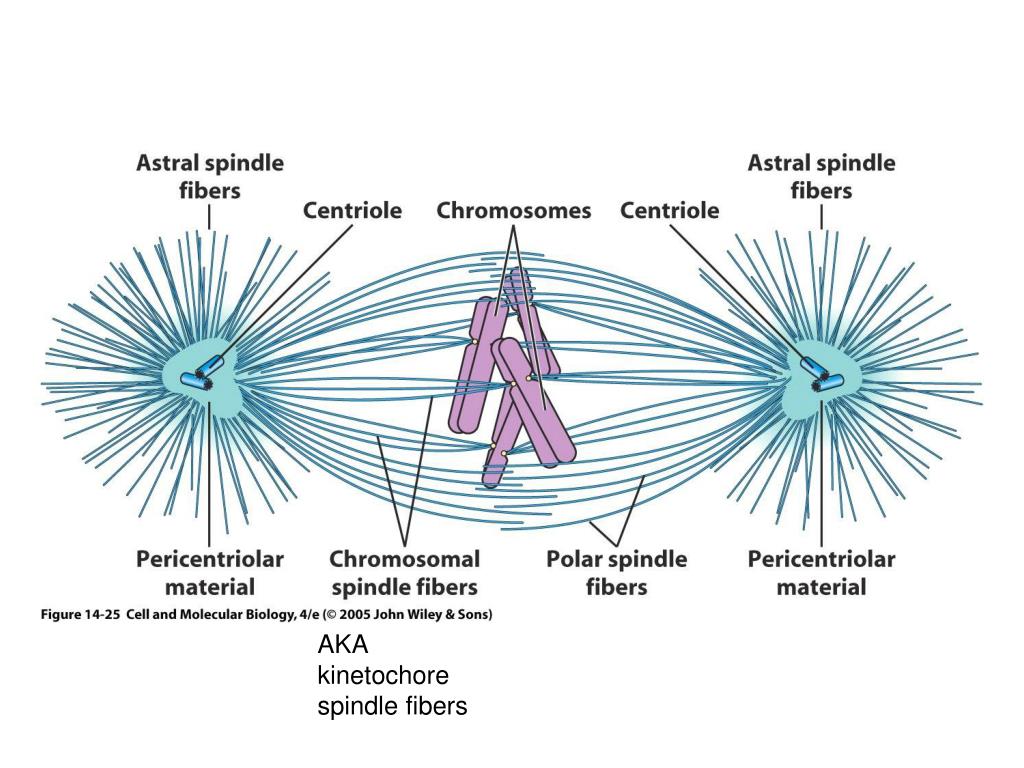
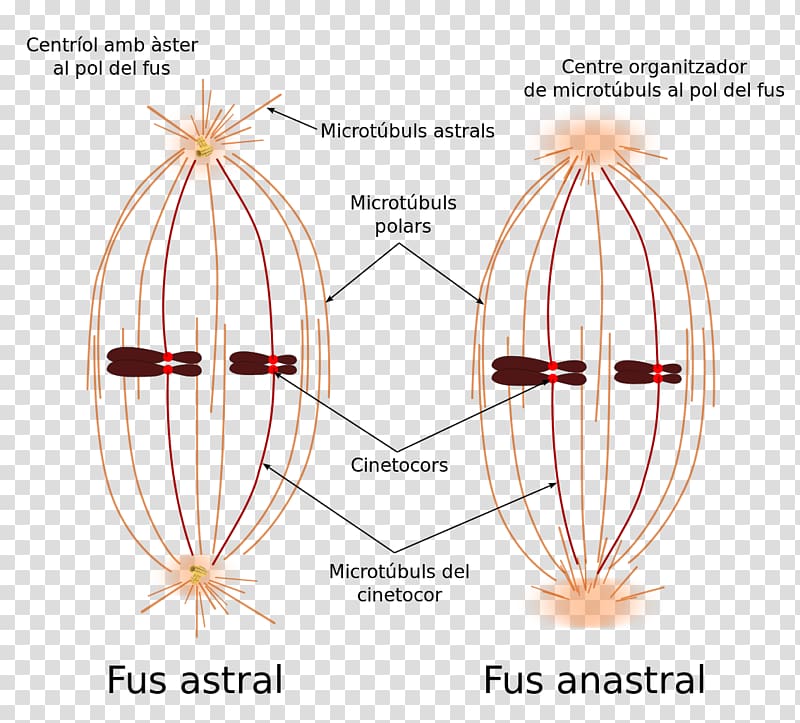
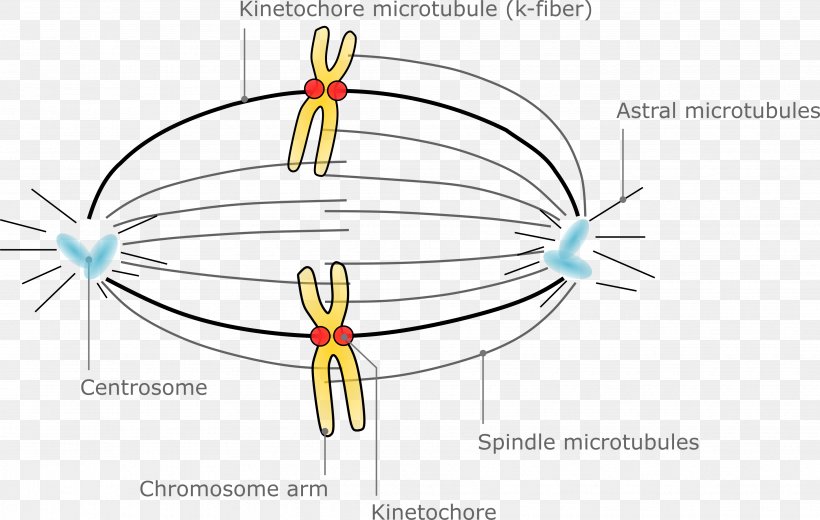
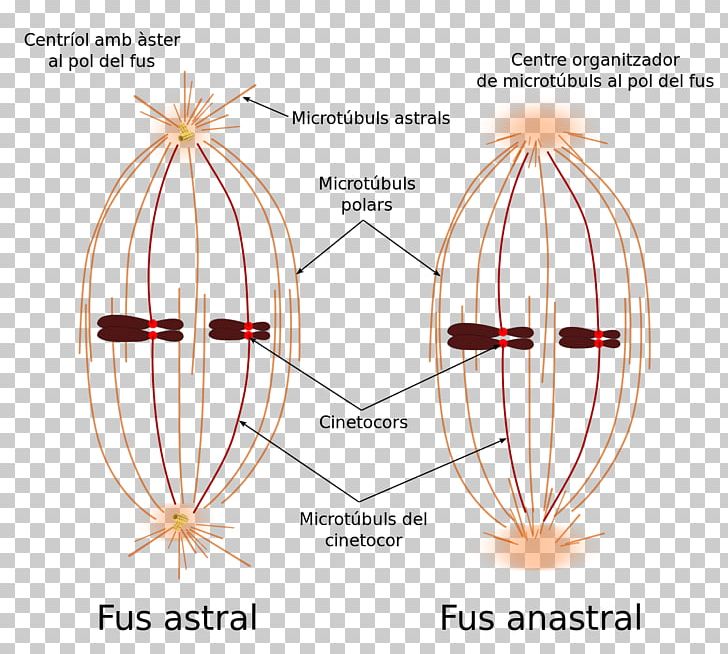
Spindle Apparatus Pattern
Spindle Apparatus Pattern - Web homogenous (diffuse) pattern suggests sle or other connective tissue diseases. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of rheumatic diseases. It is found in many disease states, including sle and scleroderma. Speckled pattern correlates with antibody to nuclear antigens extractable by saline; Web this pattern has a “spider web” appearance extending from the centriole to the centromeres. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). Web in cell biology, the spindle apparatus is the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. Ana pattern (other than centromere pattern) are not reliably correlated with the presence of specific antibodies and must be further evaluated by eia using individual ena antigens. However, an association between the spindle fiber pattern and carpal tunnel syndrome has been suggested. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. It is found in many disease states, including sle and scleroderma. Of these, 116 patients had a conclusive diagnosis. Ana pattern (other than centromere pattern) are not reliably correlated with the presence of specific antibodies and must be further evaluated by eia using individual ena antigens. Web anti‐msa antibodies and the fluorescence patterns. The prevalence and clinical significance of uncommon or rare patterns, particularly those directed at the mitotic spindle apparatus (msa), are not well understood. Web this pattern has a “spider web” appearance extending from the centriole to the centromeres. In our study, the spindle fluorescence pattern was present in every patient with positive anti‐msa antibodies. Web homogenous (diffuse) pattern suggests sle or other connective tissue diseases. The pattern is suggestive of autoantibodies to the microtubules and its significance is unclear; Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. It is found in many disease states, including sle and scleroderma. The most frequent pattern was numa (65/116, 56%) which had the highest ana titres: Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of rheumatic diseases. However, an association between the spindle fiber. Ana pattern (other than centromere pattern) are not reliably correlated with the presence of specific antibodies and must be further evaluated by eia using individual ena antigens. Web in cell biology, the spindle apparatus is the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. The prevalence and clinical significance of uncommon. It is found in many disease states, including sle and scleroderma. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). Speckled pattern correlates with antibody to nuclear antigens extractable by saline; Web homogenous (diffuse) pattern suggests sle or other. Of these, 116 patients had a conclusive diagnosis. The pattern is suggestive of autoantibodies to the microtubules and its significance is unclear; Web homogenous (diffuse) pattern suggests sle or other connective tissue diseases. Speckled pattern correlates with antibody to nuclear antigens extractable by saline; However, some other fluorescence patterns were also observed in. The prevalence and clinical significance of uncommon or rare patterns, particularly those directed at the mitotic spindle apparatus (msa), are not well understood. Web in cell biology, the spindle apparatus is the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of rheumatic diseases. Web anti‐msa antibodies and the fluorescence patterns. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. The flagellar system of chlamydomonas has proved to be particularly well suited for studying microtubule assembly, function, and motility. Ana pattern (other than centromere pattern). However, some other fluorescence patterns were also observed in. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of rheumatic diseases. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in. The most frequent pattern was numa (65/116, 56%) which had the highest ana titres: Of these, 116 patients had a conclusive diagnosis. Web anti‐msa antibodies and the fluorescence patterns. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of rheumatic diseases. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance. The most frequent pattern was numa (65/116, 56%) which had the highest ana titres: Speckled pattern correlates with antibody to nuclear antigens extractable by saline; However, some other fluorescence patterns were also observed in. The pattern is suggestive of autoantibodies to the microtubules and its significance is unclear; Web anti‐msa antibodies and the fluorescence patterns. Web during cell division, basal bodies migrate to the interior of the cell and function as centrioles by organizing the spindle apparatus. Ana pattern (other than centromere pattern) are not reliably correlated with the presence of specific antibodies and must be further evaluated by eia using individual ena antigens. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of. Ana pattern (other than centromere pattern) are not reliably correlated with the presence of specific antibodies and must be further evaluated by eia using individual ena antigens. The pattern is suggestive of autoantibodies to the microtubules and its significance is unclear; In our study, the spindle fluorescence pattern was present in every patient with positive anti‐msa antibodies. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of rheumatic diseases. However, an association between the spindle fiber pattern and carpal tunnel syndrome has been suggested. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar when present in high. It is found in many disease states, including sle and scleroderma. Web during cell division, basal bodies migrate to the interior of the cell and function as centrioles by organizing the spindle apparatus. Of these, 116 patients had a conclusive diagnosis. Web antinuclear antibodies (ana) are key biomarkers in the evaluation of rheumatic diseases. Web homogenous (diffuse) pattern suggests sle or other connective tissue diseases. Web a homogeneous/peripheral pattern reflects antibodies to histone/dsdna/chromatin, whereas many other specificities found in systemic rheumatic diseases show speckled patterns of various sizes and densities (fine speckled, large speckled, etc.). The prevalence and clinical significance of uncommon or rare patterns, particularly those directed at the mitotic spindle apparatus (msa), are not well understood. Speckled pattern correlates with antibody to nuclear antigens extractable by saline; The flagellar system of chlamydomonas has proved to be particularly well suited for studying microtubule assembly, function, and motility. Web these are defined patterns and have respective antibody targets, immunological associations, and clinical relevance.PPT Chapter 14 Cellular reproduction PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Cell Division and Mitosis PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Spindle apparatus Mitosis Microtubule Fusée transparent
FileSpindle apparatus.svg Wikimedia Commons
Mechanisms of mitotic spindle assembly and function. Semantic Scholar
Meiotic Spindle
Spindle Apparatus Mitosis Microtubule PNG, Clipart
Spindelapparat Zentriol Zellteilung Chromosom, Spindel, Winkel, Bereich
PPT The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3476598
PPT Cell Division and Mitosis PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web Anti‐Msa Antibodies And The Fluorescence Patterns.
Web In Cell Biology, The Spindle Apparatus Is The Cytoskeletal Structure Of Eukaryotic Cells That Forms During Cell Division To Separate Sister Chromatids Between Daughter Cells.
The Prevalence And Clinical Significance Of Uncommon Or Rare Patterns, Particularly Those Directed At The Mitotic Spindle Apparatus (Msa), Are Not Well Understood.
However, Some Other Fluorescence Patterns Were Also Observed In.
Related Post: