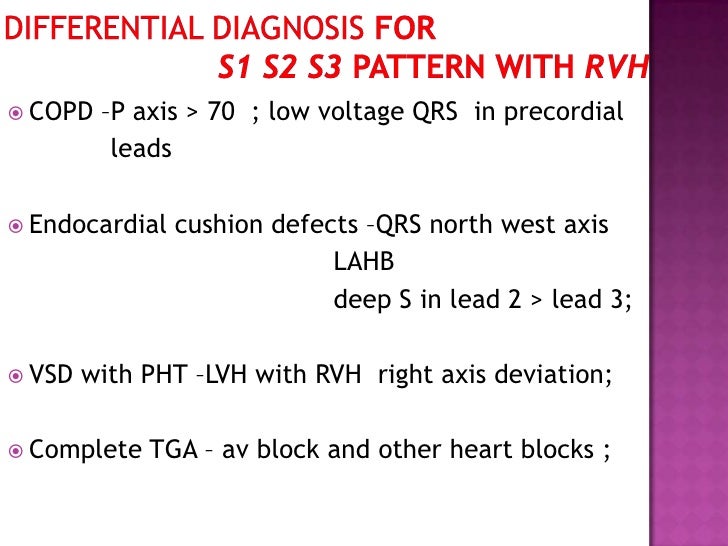
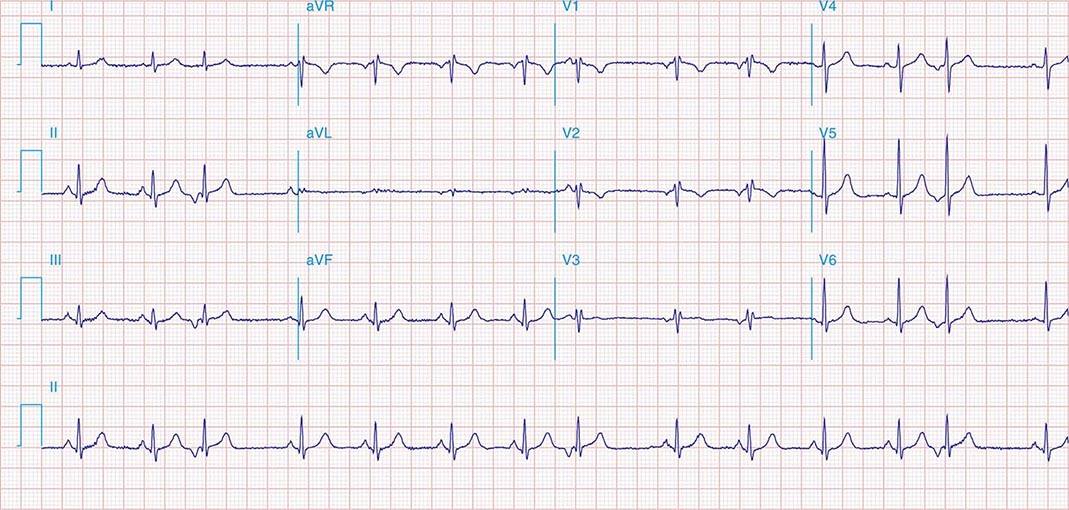
S1 S2 S3 Pattern
S1 S2 S3 Pattern - Web herbaceous or shrubby palustrine communities in floodplains or depressions; An s wave deeper than r in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of rvh; Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude, while. Web the s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome may be within normal limits in children but in adults raises the posibility of right ventricular enlargement. Web the data obtained using body surface potential mapping suggest that an anomalous wavefront rightward and superiorly oriented is present in the s1s2s3. Other features of rvh are present, including right axis deviation, and a. Web the s 1 s 2 s 3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude,. Web the sacroplasty procedure involves: Web four criteria were found to be most reliable: Stainless steel appliances, new cabinets, subway tile backsplash, faux granite countertops, upgraded. Web the sacroplasty procedure involves: Web right ventricular strain pattern due to rvh: Web an s1, s2, s3 pattern, which may mimic a left anterior hemiblock, is frequently associated with the brugada repolarization abnormalities and most likely. Learn how to diagnose right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh) from ecg features such as right axis deviation, dominant r wave in v1, dominant s wave in v5 or v6, and right ventricular strain pattern. Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude,. Web the s1 s2 s3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. The s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome is not an. Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude, while. An s wave deeper than r in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of rvh; Web the s1 s2 s3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. See examples of rvh in different conditions and compare with left ventricular hypertrophy. Learn how to diagnose right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh) from ecg features such as right axis deviation, dominant r wave in v1, dominant s wave in v5 or v6, and right ventricular strain pattern. Web. Web herbaceous or shrubby palustrine communities in floodplains or depressions; Web the data obtained using body surface potential mapping suggest that an anomalous wavefront rightward and superiorly oriented is present in the s1s2s3. Web in children an s1 s2 s3 pattern (i.e. The s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome is not an. Some apply this term to all cases. An s wave deeper than r in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of rvh; Web four criteria were found to be most reliable: Learn how to diagnose right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh) from ecg features such as right axis deviation, dominant r wave in v1, dominant s wave in v5 or v6, and right ventricular strain pattern. Web. Web the s 1 s 2 s 3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. Canopy trees, if present, very sparse and often stunted (includes low canopied sloughs), includes:. Other features of rvh are present, including right axis deviation, and a. Stainless steel appliances, new cabinets, subway tile backsplash, faux granite countertops, upgraded. Learn how to diagnose right ventricular. Web the sacroplasty procedure involves: Web in children an s1 s2 s3 pattern (i.e. Web the s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome may be within normal limits in children but in adults raises the posibility of right ventricular enlargement. Canopy trees, if present, very sparse and often stunted (includes low canopied sloughs), includes:. Web an s1, s2, s3 pattern,. Web the s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome may be within normal limits in children but in adults raises the posibility of right ventricular enlargement. Web the s1 s2 s3 pattern in the electrocardiogram has been variously defined. Web an s1, s2, s3 pattern, which may mimic a left anterior hemiblock, is frequently associated with the brugada repolarization abnormalities. Rv strain can be seen in leads v1 and v2 but also in leads 2,3,. An s wave deeper than r in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of rvh; These four simple ecg criteria can be used. Percutaneously inserting one or more bone needles into the sacrum under fluoroscopy and/or ct visual guidance. Some apply this term. These four simple ecg criteria can be used. Other features of rvh are present, including right axis deviation, and a. Web the data obtained using body surface potential mapping suggest that an anomalous wavefront rightward and superiorly oriented is present in the s1s2s3. Rv strain can be seen in leads v1 and v2 but also in leads 2,3,. See examples. Web the sacroplasty procedure involves: Web four criteria were found to be most reliable: Web the s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome may be within normal limits in children but in adults raises the posibility of right ventricular enlargement. Rv strain can be seen in leads v1 and v2 but also in leads 2,3,. Web the s 1 s. Web an s1, s2, s3 pattern, which may mimic a left anterior hemiblock, is frequently associated with the brugada repolarization abnormalities and most likely. See examples of rvh in different conditions and compare with left ventricular hypertrophy. Web four criteria were found to be most reliable: Percutaneously inserting one or more bone needles into the sacrum under fluoroscopy and/or ct. Web four criteria were found to be most reliable: Some apply this term to all cases with an s wave in each standard lead, regardless of magnitude, while. The s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome is not an. Web the data obtained using body surface potential mapping suggest that an anomalous wavefront rightward and superiorly oriented is present in the s1s2s3. Web the sacroplasty procedure involves: See examples of rvh in different conditions and compare with left ventricular hypertrophy. Web the s 1, s 2, s 3 syndrome may be within normal limits in children but in adults raises the posibility of right ventricular enlargement. Canopy trees, if present, very sparse and often stunted (includes low canopied sloughs), includes:. Other features of rvh are present, including right axis deviation, and a. Stainless steel appliances, new cabinets, subway tile backsplash, faux granite countertops, upgraded. An s wave deeper than r in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of rvh; Rv strain can be seen in leads v1 and v2 but also in leads 2,3,. Web herbaceous or shrubby palustrine communities in floodplains or depressions; Web in children an s1 s2 s3 pattern (i.e. Web right ventricular strain pattern due to rvh: Percutaneously inserting one or more bone needles into the sacrum under fluoroscopy and/or ct visual guidance.Ecg criteria of chamber enlargement
ECG Congenital Heart Disease
XRD pattern of samples S1, S2, S3 as deposited and S3 after the thermal
Ecg skills enhancement
Description, criteria, and example of the different QRS morphologies
Standard (S1, S2, S3) and alternate (A1, A2, A3) ECG electrode
Atlas of Electrocardiography Basicmedical Key
ECG Congenital Heart Disease
1. XRD diffraction pattern of synthesized ZnONPs of sample S1, S2 and
Xray diffraction pattern of S1, S2, S3, and S4 Download Scientific
Web An S1, S2, S3 Pattern, Which May Mimic A Left Anterior Hemiblock, Is Frequently Associated With The Brugada Repolarization Abnormalities And Most Likely.
Learn How To Diagnose Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (Rvh) From Ecg Features Such As Right Axis Deviation, Dominant R Wave In V1, Dominant S Wave In V5 Or V6, And Right Ventricular Strain Pattern.
These Four Simple Ecg Criteria Can Be Used.
Web The S1 S2 S3 Pattern In The Electrocardiogram Has Been Variously Defined.
Related Post: